Online Dispute Resolution in BC: Case Study #2
Intro | Part 1 | Part 2 | Part 3a | Part 3b
Our last Online Dispute Resolution (ODR) case study showcased Consumer Protection BC’s online platform.

We have an update: the platform will be used as an early resolution tool for select BC-licensed debt collection agencies. Their aim is to help consumers who don’t feel comfortable speaking to debt collectors over the phone, and who would rather communicate online.
Visit Consumer Protection BC’s blog page for more info on the debt collection pilot project.
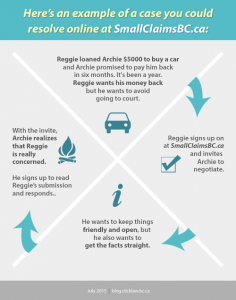
We now continue with our ODR series, this time focusing on Small Claims BC.
British Columbians who have disputes where the amount is no more than $25,000 turn to Small Claims Court to find a resolution. However, on average, claims take over a year to reach a judgment.
SmallClaimsBC.ca provides British Columbians with an alternative way to settle disputes without going to court using their ODR platform. Using ODR can help save time and money, which make sense as priorities when you are disputing a smaller amount.
New users to the platform will be asked a series of questions to create an online profile before starting their claim. If you already have an account set up as a “returning user”, you need only enter your credentials to access the dashboard.
Enter your information to complete your online account. This creates a dashboard where your claim(s) can be accessed and managed.